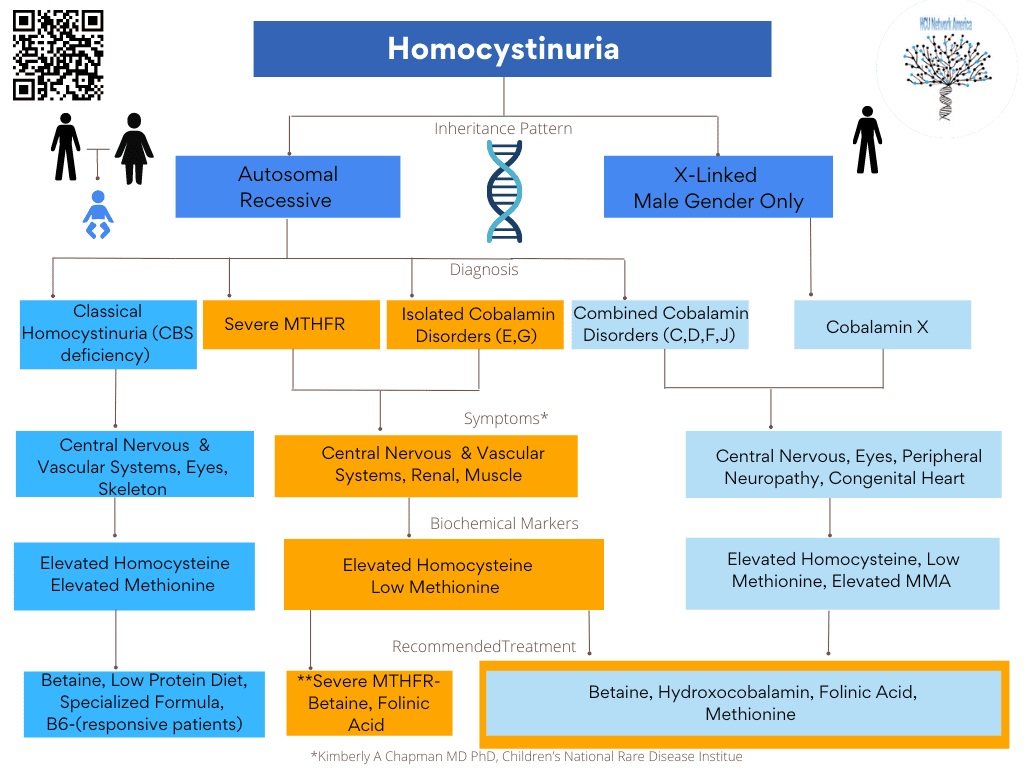
Homocystinuria is elevation of the amino acid, homocysteine (protein building block coming from our diet) in our urine. Homocysteine can also be elevated in blood. The common reasons for this are:
1) Problems with the enzyme cystathionine beta synthase (CBS), which converts homocysteine to the amino acid cystathionine (which then becomes cysteine) and needs the vitamin B6 (pyridoxine). People who have this problem have B6 deficiency or Classical (B6-responsive or non-B6-reponsive) Homocystinuria (ICD10: E72.11 )
2) Problems with converting homocysteine to the amino acid methionine. These are called “remethylation defects” since this is the process necessary for this conversion.
3) Problems with vitamin B12 or folate (usually not enough, not absorbed from stomach and gut, or not processed to help our body correctly).
High homocysteine (>120 mcmol/L) can lead to blood clots in our lungs, brain, etc.
People can have these problems from birth through their genetics (that which we inherited from our mother and father) or can be acquired.
The patient support group , HCU Network America, provides support for patients and families who have had these problems from birth as well as those diagnosed later in life. If you think you have elevated homocysteine, see your doctor and be tested.
Acquired forms of elevated homocysteine are usually due to not enough of the vitamins (pyridoxine or B6, vitamin B12, or folate) in our diets or due to the inability of our stomach system from absorbing it from out diet. Your doctor will work with you to assure you take enough but not too much of these vitamins to ensure normal levels, since even vitamins can be dangerous at high levels.