Classical HCU Therapeutic Avenues
The current therapeutic objective is described in the Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency. Click here to view the Guidelines.
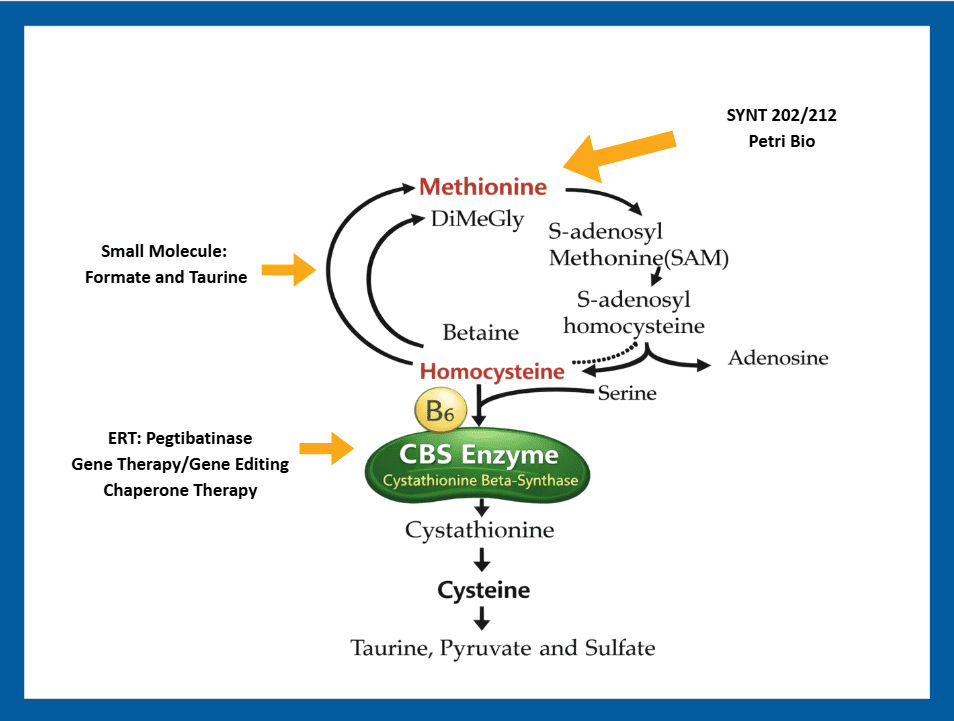
There are several approaches being investigated for the treatment of classical homocystinuria. See our Investigational Therapies Research Map.
ENZYME THERAPIES TO DEGRADE HOMOCYSTEINE
- Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) is a treatment that replaces an enzyme in a patient where the enzyme is defective due to a genetic defect. The product currently in development for classical homocystinuria, pegtibatinase (Sponsor: Travere Therapeutics), is a synthetic recombinant version of the cysteine beta synthase or CBS enzyme and is expected to be administered by subcutaneous injection. This enzyme is designed to do what CBS does, convert homocysteine directly to cysteine, to hopefully restore the normal biochemical pathway.
- The safety and effectiveness of ERT has been shown in the treatment of some lysosomal storage diseases including Gaucher disease type I, Fabry disease, MPS I (Hurler syndrome), MPS II, MPS VI, and Pompe. ERT does not correct the underlying genetic defect and is not a curative approach but rather requires lifelong administration.
ORAL (GI) THERAPIES TO PREVENT ABSORPTION OF METHIONINE
-
- An engineered methionine-gamma-lyase enzyme is being developed by Syntis, SYNT 202. This is an orally administered, GI-stable therapeutic enzyme to potentially treat HCU by degrading methionine from food/protein intake in the GI tract, so that the methionine is not absorbed and converted to homocysteine.
-
- This product would need to be taken daily with lifelong administration. An extended-release formulation is also in development which may allow once-daily dosing.
- A methionase enzyme that is derived from bacteria is being developed by Petri Bio. This is an orally administered, GI-stable therapeutic enzyme to potentially treat HCU by degrading methionine from food/protein intake in the GI tract, so that the methionine is not absorbed and converted to homocysteine.
- This product would need to be taken daily with lifelong administration.
GENETIC THERAPY: DELIVER OR EDIT DNA TO ENABLE BODY TO PRODUCE CBS ENZYME
CHAPERONE THERAPY: ADMINISTER SMALL MOLECULES (USUALLY ORAL THERAPIES) TO RESTORE ENZYME ACTIVITY
- Small molecules can be chemically synthesized and often taken in tablet or capsule form, in contrast to enzymes or other “biologics”, which are made via living organisms and too “large” to be taken in tablet or capsule form so require injection or infusion. There was a screening project recently completed, funded by a grant from HCU Network America, to identify small molecules that would activate the function of the CBS enzyme thereby increasing its effectiveness in lowering homocysteine levels. Follow-on work is now being funded by an unnamed pharmaceutical or biotech company.
- Any product resulting from this research would be expected to be administered on a daily basis for lifelong administration
METABOLIC PATHWAY MODIFICATION:
Here is a schematic overview showing the biochemical cascade and how emerging therapeutic interventions address the biochemical or disease process.